T3 (or Cytomel) can greatly increase the metabolic rate and speed up the cell’s metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. If the body cannot secrete enough thyroid hormone, such as hypothyroidism, the metabolic rate cannot be normal. People with hypothyroidism usually gain fat, find it extremely difficult to lose fat, lose energy, and even lose hair. These problems can be solved with T3.
The dose of T3 used to treat hypothyroidism is generally not large, and it may not accelerate fat loss, but it can restore the metabolic rate to normal. Athletes will increase the dose to directly accelerate fat loss. T3 (Cytomel) combined with a calorie-controlled diet will greatly accelerate the fat loss process. Although very effective, T3 (Cytomel) is best used with steroids. T3 is one of the strongest fat-reducing drugs, but it directly consumes ATP, making the user sleepy and weak. High doses of T3 and reduced ATP can cause muscle loss. The body will consume various things to meet energy needs at this time, including muscle, so it is very necessary to use anabolic steroids when using T3.
T3 benefits (Cytomel):
Whether you are a hypothyroid patient or an athlete, you can lose fat by using T3 (Cytomel). Using T3 restores the metabolic rate of hypothyroid patients to normal levels, and athletes can lose fat faster by taking T3.
After using T3 (Cytomel), you still have to control calories and eat healthily. The principle of consuming more than you consume during the fat loss period has not changed. If you eat more than you consume, it doesn’t matter how much T3 you use. However, if you use T3, you can consume more calories because the extra hormone increases the metabolic rate and can consume more calories.
T3 and growth hormone HGH (especially high doses) have many benefits. Data show that high doses of growth hormone HGH will reduce the secretion of T3. Although it is not necessary to supplement exogenous T3 at this time, it is meaningful to use it. In any case, using T3 and growth hormone to lose fat is definitely much faster, and it will be even faster if the beta-2 stimulator clenbuterol is added.
T3 Side effects:
Generally speaking, healthy adults can safely tolerate it, and so can those with hypothyroidism. Side effects are usually caused by high doses or overdose. Everyone’s drug reaction is different. Possible side effects include:
Headache
Sweating
Irregular heartbeat
Anxiety
Increased bowel movements
Menstrual disorders
Extremely high doses may cause the following problems:
Angina
Shock
Congestive heart failure
Hyperthyroidism
In general, T3 is very safe, but long-term high doses or even overdose can threaten life and health.
Another side effect is hypothyroidism. Many people worry that they will have hypothyroidism after stopping the drug. They believe that after stopping exogenous 3, the body’s own secretion will not be enough, which will lead to fat gain. Although it is possible, it is almost impossible if used correctly. Proper use is not only about dosage and duration of medication, but also about how to stop the drug. It cannot be stopped suddenly and completely. The user should reduce the dose and maintain it for a period of time, not too long, to ensure that the thyroid hormone returns to normal. Recovery is not a problem for healthy adults who use the drug correctly.
How to use T3:
The dose of T3 (Cytomel) to treat hypothyroidism starts at 25 micrograms per day. After a few weeks, the patient goes for a follow-up examination and can increase it by 25 micrograms per day. After two weeks, you can increase to 75 micrograms per day until you find a suitable maintenance dose.
Generally speaking, it is in the range of 25-75 micrograms per day. You don’t need to take it in divided doses, you can take the whole dose at once.
The dosage of T3 used by athletes is similar to the medical dosage. Generally, you start with 25 micrograms per day and increase it by 12.5-25 micrograms every two to four weeks. Most people don’t need to exceed 75-100 micrograms per day. 125 micrograms per day can only be sustained for a short period of time. This dose should only be used in the final stage of a pre-competition fat loss plan. The entire duration of medication is safest for six to eight weeks. Eight to thirteen weeks is also acceptable, but it increases the risk of thyroid dependence. However, most healthy adults are fine. After reaching the high dose, you should be ready to stop the medication. Reduce the dose to 25 micrograms per day for seven to ten days so that the body can adjust and prevent hypothyroidism. Don’t stop the medication suddenly.
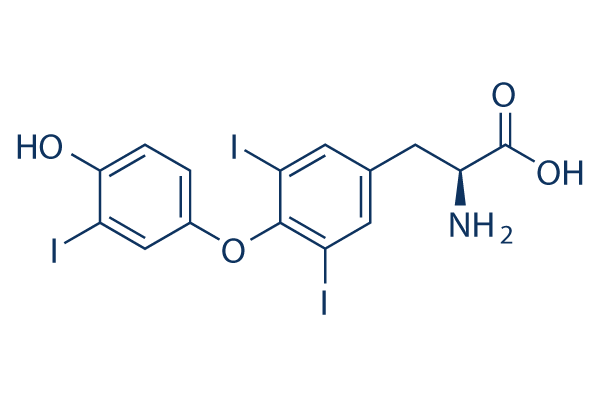
Liothyronine sodium Chemical Properties
Melting point 205 °C (dec.)(lit.)
alpha 20 º (c=2,alcohol/1.2N HCl)
RTECS YP2836500
storage temp. -20°C
solubility 4 M NH4OH in methanol: 125 g/5mL, clear, yellow-brown
form powder
color White to Pale Brown
Water Solubility Partly miscible in water. Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, methanol, sodium hydroxide and ethanol. Practically insoluble in most other organic solvents.
Sensitive Light Sensitive
Merck 5510
BRN 8179867
InChI InChI=1/C15H12I3NO4.Na/c16-9-6-8(1-2-13(9)20)23-14-10(17)3-7(4-11(14)18)5-12(19)15(21)22;/h1-4,6,12,20H,5,19H2,(H,21,22);/q;+1/p-1/t12-;/s3
InChIKey SBXXSUDPJJJJLC-ZLBVLXFENA-M
SMILES C1(C(I)=CC(C[C@H](N)C([O-])=O)=CC=1I)OC1=CC=C(O)C(I)=C1.[Na+] |&1:6,r|
CAS DataBase Reference 55-06-1(CAS DataBase Reference)
EPA Substance Registry System L-Tyrosine, O-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenyl)-3,5-diiodo-, monosodium salt (55-06-1)