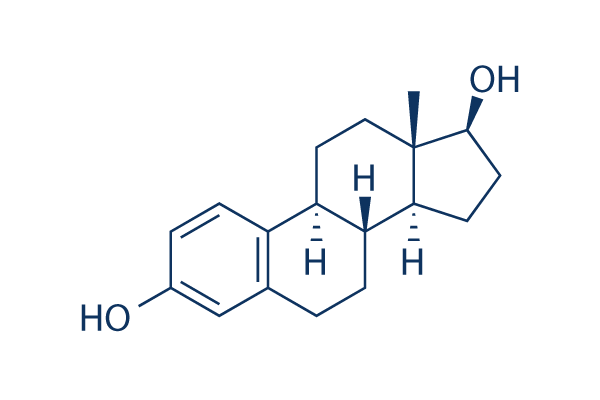
what is Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of female reproductive cycles such as estrous and menstrual cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as the breasts, widening of the hips and a female pattern of fat distribution. It is also important in the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues such as the mammary glands, uterus and vagina during puberty, adulthood and pregnancy. It also has important effects in many other tissues including bone, fat, skin, liver, and the brain.
Though estradiol levels in males are much lower than in females, It has important roles in males as well. Apart from humans and other mammals, It is also found in most vertebrates and crustaceans, insects, fish, and other animal species.
It is produced especially within the follicles of the ovaries, but also in other tissues including the testicles, the adrenal glands, fat, liver, the breasts, and the brain. It is produced in the body from cholesterol through a series of reactions and intermediates. The major pathway involves the formation of androstenedione, which is then converted by aromatase into estrone and is subsequently converted into estradiol. Alternatively, androstenedione can be converted into testosterone, which can then be converted into It. Upon menopause in females, production of estrogens by the ovaries stops and estradiol levels decrease to very low levels.
In addition to its role as a natural hormone, estradiol is used as a medication, for instance in menopausal hormone therapy and feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women; for information on estradiol as a medication, see the estradiol (medication) article.buy Estradiol wholesale
Sexual development
See also: Breast development § Biochemistry
The development of secondary sex characteristics in women is driven by estrogens, to be specific, estradiol. These changes are initiated at the time of puberty, most are enhanced during the reproductive years, and become less pronounced with declining estradiol support after menopause. Thus, It produces breast development, and is responsible for changes in the body shape, affecting bones, joints, and fat deposition. In females, estradiol induces breast development, widening of the hips, a feminine fat distribution (with fat deposited particularly in the breasts, hips, thighs, and buttocks), and maturation of the vagina and vulva, whereas it mediates the pubertal growth spurt (indirectly via increased growth hormone secretion) and epiphyseal closure (thereby limiting final height) in both sexes.
Reproduction
Female reproductive system
In the female, It acts as a growth hormone for tissue of the reproductive organs, supporting the lining of the vagina, the cervical glands, the endometrium, and the lining of the fallopian tubes. It enhances growth of the myometrium. It appears necessary to maintain oocytes in the ovary. During the menstrual cycle, estradiol produced by the growing follicles triggers, via a positive feedback system, the hypothalamic-pituitary events that lead to the luteinizing hormone surge, inducing ovulation. In the luteal phase, It, in conjunction with progesterone, prepares the endometrium for implantation. During pregnancy, estradiol increases due to placental production. The effect of estradiol, together with estrone and estriol, in pregnancy is less clear. They may promote uterine blood flow, myometrial growth, stimulate breast growth and at term, promote cervical softening and expression of myometrial oxytocin receptors.[citation needed] In baboons, blocking of estrogen production leads to pregnancy loss, suggesting estradiol has a role in the maintenance of pregnancy. Research is investigating the role of estrogens in the process of initiation of labor. Actions of estradiol are required before the exposure of progesterone in the luteal phase.estradiol side effects
Male reproductive system
The effect of estradiol (and estrogens in general) upon male reproduction is complex. Estradiol is produced by action of aromatase mainly in the Leydig cells of the mammalian testis, but also by some germ cells and the Sertoli cells of immature mammals. It functions (in vitro) to prevent apoptosis of male sperm cells. While some studies in the early 1990s claimed a connection between globally declining sperm counts and estrogen exposure in the environment, later studies found no such connection, nor evidence of a general decline in sperm counts.[ Suppression of estradiol production in a subpopulation of subfertile men may improve the semen analysis.
Males with certain sex chromosome genetic conditions, such as Klinefelter’s syndrome, will have a higher level of estradiol.Estradiol for sale
description β-Estradiol is an endogenous estrogenic hormone receptor (ER) agonist (Ki values are 0.12 and 0.13 nM for ERα and ERβ respectively). Also high affinity ligand at membrane estrogen GPR30 receptors. β-Estradiol is an activator of PI 3-kinase.
Estradiol (17β-estradiol, β-Estradiol, E2, 17β-Oestradiol) is a human sex hormone and steroid, and the primary female sex hormone. It upregulates IL-6 expression through the estrogen receptor β (ERβ) pathway.
Uses 17β-Estradiol is the major estrogen secreted by the premenopausal ovary.This compound is a contaminant of emerging concern (CECs). Drinking water contaminant candidate list 3 (CCL 3) compound as per United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), environmental, and food contaminants.
β-Estradiol is used to study cell differentiation and transformations (tumorigenicity).
Indications and Usage It is a white or milky white ordorless crystalline powder. It is soluble in dioxane and acetone, slightly soluble in ethanol, and insoluble in water.
It is the intermediate between estradiol valerate and estradiol benzoate, also is a type of estrogen drug. It can be used to treat uterine functional bleeding, primary amenorrhea, menopausal syndrome, and prostate cancer. Estradiol can promote and adjust the normal growth of female sex organs and secondary sex characteristics, promote mammary duct maturation and growth, and aid in posseting. Estradiol can also be used in biochemical research.
Adverse reactions In high dosages, estradiol can inhibit the release of anterior pituitary prolactin, thus decreasing breast milk secretion. However, nausea, vomiting and endometrial hyperplasia-induced bleeding may occur. Patients with liver or kidney failure should use with caution.
Contradictions Do not use on breasts, vaginal area and vaginal mucosa.
Description Estradiol, 17-beta- is an odorless white to yellow crystalline substance. Molecular weight = 272.42;Boiling point = (decomposes); Freezing/Meltingpoint = 173 – 179℃. Hazard Identification (based onNFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 2, Flammability 1,Reactivity 0. Insoluble in water.
Chemical Properties White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Chemical Properties Estradiol, 17-β-is an odorless white to yellow crystalline substance.
Uses 17β-Estradiol is the major estrogen secreted by the premenopausal ovary.This compound is a contaminant of emerging concern (CECs). Drinking water contaminant candidate list 3 (CCL 3) compound as per United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), environmental, and food contaminants.
Uses Estradiol USP (Estrace) is used to treat Breast cancer; prostatic carcinoma.
Application β-Estradiol has been used:
for the in vitro maturation of bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs)
as a supplement in in vitro maturation medium (IVM), which is used as a control medium
in estrogen-induction assay
Definition ChEBI: The 17beta-isomer of It.
Acquired resistance Estradiol is the most potent endogenous estrogen, exhibiting high affinity for the ER and high potency when administered parenterally. When administered orally, It is promptly conjugated in the intestine and oxidatively metabolized by the liver, resulting in its low oral bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness.
General Description Estradiol, estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol, is the most activeof the natural steroid estrogens. Although its 17β-OHgroup is vulnerable to bacterial and enzymatic oxidation toestrone, it can be temporarily protected as anester at C3 or C17, or permanently protected by adding a17α-alkyl group (e.g., 17α-ethinyl estradiol, the most commonlyused estrogen in oral contraceptives). The increasedoil solubility of the 17β-esters (relative to estradiol) permitsthe esters to remain in oil at the IM injection site for extendedperiods. These derivatives illustrate the principles of steroidmodification. Transdermal estradiolproducts avoid first-pass metabolism, allowing estradiol tobe as effective as oral estrogens for treating menopausalsymptoms. A new transdermal spray, Evamist, was approvedin 2007. It itself is typically not very effective orallybecause of rapid metabolism, but an oral formulation of micronizedestradiol that allows more rapid absorption of thedrug is available (Estrace). In addition to the oral and transdermalproducts, It is also available in gel, cream, andvaginal ring formulations. The commercially available estradiolesters are the following:
Estradiol 3-acetate, USP (oral; vaginal ring)
Estradiol 17-valerate, USP (IM injection)
Estradiol 17-cypionate, USP (IM injection).
Hazard A carcinogen (OSHA).
Biological Activity Endogenous estrogen receptor (ER) agonist (K i values are 0.12 and 0.13 nM for ER α and ER β respectively). Also high affinity ligand at membrane estrogen GPR30 receptors.
Contact allergens Natural estradiol, used in transdermal systems for hormonal substitution, can induce allergic contact dermatitis, with the risk of systemic contact dermatitis after oral reintroduction.
Biochem/physiol Actions The major estrogen secreted by the premenopausal ovary. Estrogens direct the development of the female phenotype in embryogenesis and during puberty by regulating gene transcription and, thus, protein synthesis. It also induces the production of gonadotropins which, in turn, induce ovulation. Exposure to It increases breast cancer incidence and proliferation.
Mechanism of action The most potent naturally occurring estrogen in mammals. It is synthesized primarily in the ovary, and also in the testis, adrenal gland and placenta, and to a limited extent by peripheral tissues (e.g., liver, fat, and skeletal muscle) from androstenedione and testosterone. It is responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics in the female at puberty (i.e., growth and development of the vagina, uterus and fallopian tubes, enlargement of the breasts, and growth and maturation of long bones).
Safety Profile Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. A promoter. Human reproductive effects by ingestion: ferthty effects. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. A steroid hormone much used in medicine. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
β-Estradiol Chemical Properties
Melting point 178-179 °C(lit.)
alpha D25 +76 to +83° (dioxane)
Boiling point 355.44°C (rough estimate)
density 1.0708 (rough estimate)
refractive index 80.4 ° (C=1, Dioxane)
Fp 2℃
storage temp. room temp
solubility Practically insoluble in water, soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), slightly soluble in methylene chloride.
form powder
pka pKa 10.71±0.02(H2O(0.1% p-dioxane) t=25±0.1 I=0.03(KCl))(Approximate)
color White to off-white
Water Solubility Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, ethanol , water, phosphate buffer saline, dimethyl formamide, acetone, dioxane and alkali hydroxides. Slightly soluble in vegetable oils.
Merck 14,3703
BRN 1914275
BCS Class 1
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
InChIKey VOXZDWNPVJITMN-ZBRFXRBCSA-N
CAS DataBase Reference 50-28-2(CAS DataBase Reference)
NIST Chemistry Reference Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17beta-diol(50-28-2)
EPA Substance Registry System Estradiol (50-28-2)
more :https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estradiol