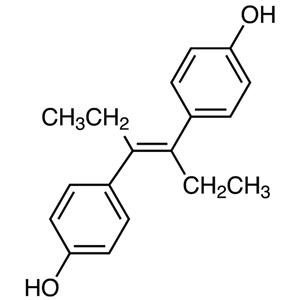
Diethylstilbestrol [Effects and Uses]
① Promote the normal development of female sexual organs and secondary sexual characteristics; ② Promote endometrial hyperplasia and vaginal epithelial keratinization; ③ Reduce systemic disorders caused by hypogonadism in women during menopause or after gynecological surgery; ④ Enhance uterine contraction and increase uterine sensitivity to oxytocin; ⑤ Stimulate with small doses and inhibit the secretion of anterior pituitary gonadotropin and prolactin with large doses; ⑥ Anti-androgenic effect.
Oral absorption is good, slowly inactivated by the liver, and metabolites are excreted from urine and feces.
Clinically used for various diseases caused by ovarian insufficiency or pituitary dysfunction, amenorrhea, uterine dysplasia, functional uterine bleeding, menopausal syndrome, senile vaginitis and milk withdrawal. It is also used for prostate cancer.
[Usage and Dosage]
Oral, 0.25 once.
1mg, 0.25-6mg per day.
1. Amenorrhea: Oral administration of a small dose to stimulate the anterior pituitary gland to secrete gonadotropin, not exceeding 0.25 mg per day.
2. For artificial menstrual cycle: Take 0.25 mg daily for 20 consecutive days, and then use the same method for treatment after menstruation, for a total of 3 cycles.
3. For prolonged menstrual cycle and uterine hypoplasia: Take 0.1-0.2 mg daily for half a year, and stop taking during menstruation.
4. Treatment of functional uterine bleeding: Take 0.5-1 mg every night for 20 consecutive days.
5. For menopausal syndrome: Take 0.25 mg daily, and change to 0.1 mg daily after the symptoms are controlled (if 5-10 mg of methyltestosterone is taken sublingually every day at the same time, the effect is better).
[Usage and Dosage]2
6. Weaning: Take 5 mg each time, 2-3 times a day, for 3 consecutive days, or intramuscular injection of 4 mg once a day, for 3-5 consecutive days, and tighten the breasts at the same time and take less fluid.
7. Senile vaginitis: vaginal suppositories, 1-2 tablets (0.2 mg each) every night, for 7 days.
8. Used in conjunction with surgery for prostate cancer: 3 mg per day, divided into 3 doses, for 2-3 months. Maintenance dose 1 mg per day.
9. Used for infertility caused by poor uterine development and thick cervical secretions; a small dose makes the cervical mucus thinner and sperm easier to penetrate, take 0.1 mg per day after menstruation, for a total of 15 days, and the course of treatment is 3-6 months.
10. Used for missed abortion (death within 7 months of pregnancy, fetal menstruation 2 months or more has not been delivered): take 5 mg each time, 3 times a day, 5-7 days as a course of treatment, stop the drug for 5 days, if ineffective, repeat the course of treatment.
[Precautions]
1. Long-term use can cause excessive endometrial hyperplasia and lead to uterine bleeding and uterine hypertrophy.
2. The drug should be taken according to the specified method, and stopping the drug midway may cause uterine bleeding.
3. It is contraindicated for patients with liver or kidney disease and pregnant women.
Chemical Properties
Melting point 170-172 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 407.1±25.0 °C(Predicted)
density 1.107±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
solubility soluble in Methanol
pka 9.27±0.15(Predicted)
form powder to crystal
color White to Almost white
Merck 14,3129
InChIKey RGLYKWWBQGJZGM-ISLYRVAYSA-N
CAS DataBase Reference 6898-97-1
Bioavailability Well-absorbed
Protein binding >95%
Metabolism Hydroxylation, oxidation, glucuronidation
Metabolites • (Z,Z)-Dienestrol
• Paroxypropione
• Glucuronides
Elimination half-life 24 hours
Excretion Urine, feces
More Introduction:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diethylstilbestrol