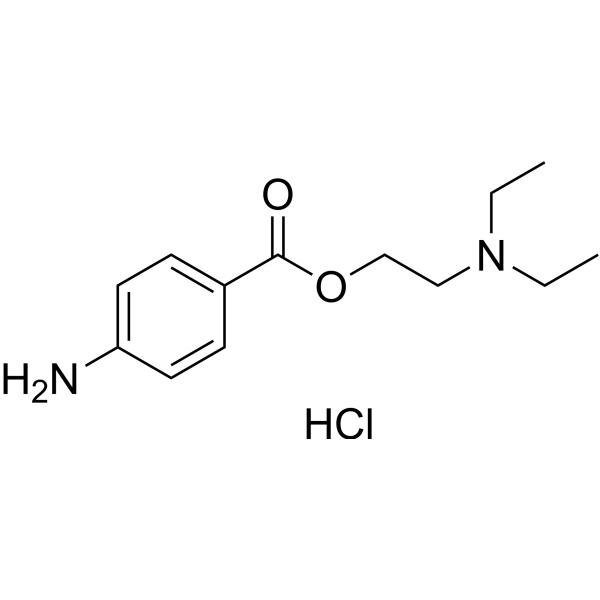
Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is most commonly used in dental procedures to numb the area around a tooth and is also used to reduce the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin. Owing to the ubiquity of the trade name Novocain or Novocaine, in some regions, procaine is referred to generically as novocaine. It acts mainly as a sodium channel blocker. Today, it is used therapeutically in some countries due to its sympatholytic, anti-inflammatory, perfusion-enhancing, and mood-enhancing effects.
Procaine was first synthesized in 1905, shortly after amylocaine. It was created by the chemist Alfred Einhorn who gave the chemical the trade name Novocaine, from the Latin nov- (meaning “new”) and -caine, a common ending for alkaloids used as anesthetics. It was introduced into medical use by surgeon Heinrich Braun.
Prior to the discovery of amylocaine and procaine, cocaine was a commonly used local anesthetic. Einhorn wished his new discovery to be used for amputations, but for this surgeons preferred general anesthesia. Dentists, however, found it very useful.
Description
Procaine hydrochloride powder, also called Novocain, or Novocaine, a topical anesthetic, which can block the nerve fiber conduction temporarilyand has a narcotic effect,strong effect, low toxicity, and non-addictive, but on the skin, mucosal penetration is weak, unsuitable for surface anesthesia, patients are used for infiltration, conduction and spinal anesthesia.
The structure of procaine hydrochloride with aromatic primary amino, easy oxidation discoloration pH, temperature, UV, oxygen and metal ions can accelerate the oxidation discoloration. The aqueous solution was stable in pH3.0~5. So preparation of procaine hydrochloride injection, it generally takes add acid to regulate pH 3.3 to 5.5, and strictly control the sterilization temperature and time. to 100 ℃ steam sterilization 30min circulation is appropriate, and should pay attention to shading, sealed save.
Chemical
Properties Procaine hydrochloride is a white crystalline, odorless powder that is freely soluble in water, but less soluble in alcohol and almost insoluble in ether; solutions acid to litmus. Because the ester bond in the structure can be hydrolyzed to produce p-aminobenzoic acid and diethylaminoethanol, under certain conditions, p-aminobenzoic acid can be further decarboxylated to produce toxic aniline. Procaine hydrochloride has aromatic primary amino groups in its structure, which can be easily oxidized and discolored. pH, temperature, ultraviolet light, oxygen and metal ions can accelerate the oxidation and discoloration.
Uses Procaine is a local anesthetic of the amino ester group that is primarily used as a topical anesthetic. Procaine is also used to control the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin as well as in dentistry.
General Description
Procaine hydrochloride is a synthetic compound that belongs to the class of local anesthetic drugs. It has a structure similar to the natural compounds that participate in nerve impulse transmission. It shows interaction with the cellular membranes causing membrane lipids to expand, membrane-bound calcium to displace and change the structure of the proteins that are responsible for regulating the cell permeability and shape.
Hazard Toxic by ingestion.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Procaine is a Na+ channel blocker, commonly used as an anesthetic agent and is considered safer than cocaine. It is also useful as a painkiller to treat pain, associated with joints and tendons.
Contact allergens Procaine is a local anesthetic with para-amino function. Sensitization mainly concerns the medical, dental, and veterinary professions.
Safety Profile Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects: acute renal fdure. May have human reproductive effects. See also ESTERS. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of HCl and NO,. Used as a local anesthetic.
Precautions
Procaine hydrochloride is used for infiltration, nerve block, peridural and spinal anest sthesia. It is considered a fairly safe drug if suitable precautions are observed. However, as with any anesthetic, idiosyncrasy may be encountered. Slow administration and avoidance of accidental intravenous injection are advisable. In local administration, if increased sensitivity to procaine is suspected, as in patients with cardiac disease or endocrine disorders (such as hyperthyroidism), an initial small dose to test tolerance is recommended.
Procaine hydrochloride Chemical Properties procaine hydrochloride wholesale
Melting point 155-156 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 195-196°C 17mm
density 1.1761 (rough estimate)
refractive index 1.5270 (estimate)
Fp 195-196°C/17mm
storage temp. 2-8°C
form Crystals or Crystalline Powder
color Colorless to white
Water Solubility soluble
Sensitive Air Sensitive
Merck 14,7757
BRN 3917802
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
InChIKey HCBIBCJNVBAKAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
LogP 2.364 (est)
CAS DataBase Reference 51-05-8(CAS DataBase Reference)
EPA Substance Registry System Procaine hydrochloride (51-05-8)
More Introduction:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Procaine