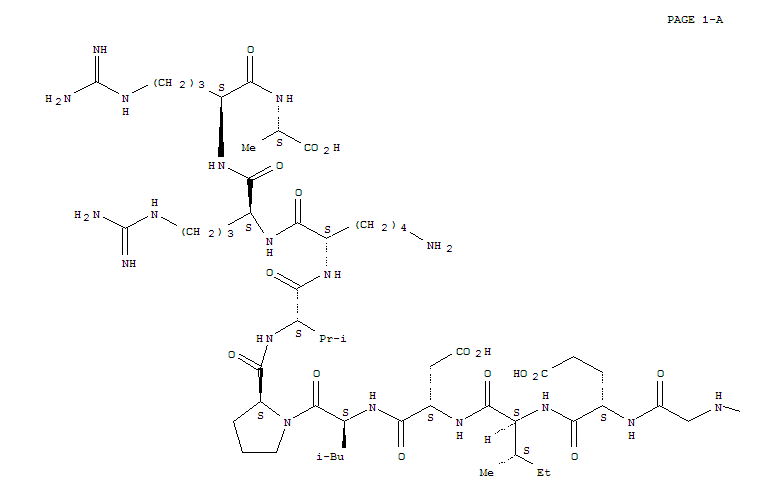
Humanin is a micropeptide encoded in the mitochondrial genome by the 16S ribosomal RNA gene, MT-RNR2. Its structure contains a three-turn α-helix, and no symmetry.
In in vitro and animal models, it appears to have cytoprotective effects.
Gene
Hum is encoded in the mitochondrial genome by the 16S ribosomal RNA gene, MT-RNR2. Multiple paralogs are found in the nuclear genome (due to nuclear mitochondrial DNA segments) and are named MTRNR2L followed by a number. It is not entirely sure whether these paralogous isoforms are completely unexpressed.
Protein
The expressed humanin peptide contains a three-turn α-helix, and has no symmetry.
The length of the peptide depends on where it is produced. If it is produced inside the mitochondria it will be 21 amino acids long. If it is produced outside the mitochondria, in the cytosol, it will be 24 amino acids long. Both peptides have been shown to have biological activity.
Interactions
Extracellular interaction with a tripartite receptor composed of gp130, WSX1, and CNTFR, as well as interaction with the formyl peptide receptor 2 (formylpeptide-like-1 receptor) have been published.
Intracellular interaction with BAX, tBID, IGFBP3, and TRIM11 may also be required for the effects of humanin.
Discovery
Hum was the first mitochondria-derived peptide to be discovered. Hum was independently found by three different labs looking at different parameters. The first to publish, in 2001, was the Nishimoto lab, which found humanin while looking for possible proteins that could protect cells from amyloid beta, a major component of Alzheimer’s disease. The Reed lab found humanin when screening for proteins that could interact with Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), a major protein involved in apoptosis. The Pinchas Cohen lab independently discovered humanin when screening for proteins that interact with IGFBP3.
Research
Experiments using cultured cells have demonstrated that humanin has both neuroprotective as well as cytoprotective effects and experiments in rodents have found that it has protective effects in Alzheimer’s disease models, Huntington’s disease models and stroke models.
Hum is proposed to have myriad neuroprotective and cytoprotective effects. Both studies in cells and rodents have both found that administration of hum or humanin derivatives increases survival and/or physiological parameters in Alzheimer’s disease models. In addition to Alzheimer’s disease, humanin has other neuroprotective effects against models of Huntington’s disease, prion disease, and stroke.
Beyond the possible neuroprotective effects, humanin protects against oxidative stress, atherosclerotic plaque formation, and heart attack. Hum activates chaperone-mediated autophagy in a dose-dependent manner. Humanin decreases production of inflammatory cytokines, which is part of its anti-apoptotic effect. Metabolic effects have also been demonstrated and humanin helps improve survival of pancreatic beta-cells, which may help with type 1 diabetes, and increases insulin sensitivity, which may help with type 2 diabetes. In rats, the hum analog appears to normalize glucose levels and reduce diabetes symptoms.
Rattin shows the same ability as humanin to defend neurons from the toxicity of beta-amyloid, the cause of degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease.
Small humanin-like peptides are a group of peptides found in the mitochondrial 16S rRNA, and also possess retrograde signaling functions.
More Introduction:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Humanin