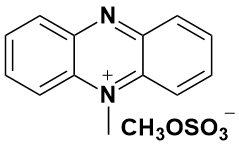
Sarm 5-Methylphenazinium methosulfate this redox-active reagent (FW = 306.34 g/mol; CAS 299-11-6; Eo’ = +0.080 V, pH = 7 and T = 30°C), also known as N-methylphenazoniummethosulfat, is frequently used as an artificial electron acceptor and carrier in studies of redox reactions. The reduced semiquinone, which may be prepared nonenzymatically from NADH or NADPH, is a colorless product (occasionally, a green color is reported) and can be used as an electron donor. This reduced compound is rapidly oxidized by dioxygen and will reduce cytochrome c, indophenol dyes, and many other electron acceptors. It is often used with ascorbic acid to determine nitric oxide reductase activity.
Enzyme inhibitor
Action as a Redox Substrate:5-Methylphenazinium methosulfate, Phenazine methosulfate (MTT) is a synthetic electron acceptor substtrate for many enzymes (e.g., succinate dehydrogenase, holine dehydrogenase, glycolate dehydrogenase, polyvinyl alcohol dehydrogenase, (R)-pantolactone dehydrogenase, formate dihydro genase, isoquinoline 1-oxidoreductase, quinaldate 4-oxidoreductase, aralkylamine dehydrogenase, glycine dehydrogenase (cyanide-forming), trimethylamine dehydrogenase, cytokinin dehydrogenase, and 4-cresol dehydrogenase (hydroxylating). When used in enzyme assays, MTT is converted to formazin, an intensely purple-colored product. To achieve high-sensitivity and a linear dependence, one must use a solubilization solution (usually either dimethyl sulfoxide, an acidified ethanol solution, or a solution of the detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate in diluted hydrochloric acid) to disperse/dissolve the otherwise insoluble formazan to obtain colored suspension/solution. The absorbance of this solution may then be quantified by measuring the wavelength between 500 and 600 nm in a spectrophotometer.
Enzyme inhibitor 2
The degree of light absorption depends on the solvent. Cell Viability Asaays: MTT has been widely employed in colorimetric assays for assessing the viability of cells. When tested under defined conditions, NAD(P)H-dependent cellular oxidoreductase enzymes catalyze the conversion of MTT to formazan, the intensity of which indicates cell viability. Other related tetrazolium dyes (including XTT, MTS and the WSTs) are used in conjunction with the intermediate electron acceptor, 1- methoxy phenazine methosulfate (PMS). Target(s): ferredoxin:NADPcyclase; photophosphorylation; progesterone monooxygenase; protein-Np -phosphohistidine:sugar phosphotransferase; stearoyl-CoA 9- desaturase; steroid 9a-monooxygenase; steroid 11b monooxygenase; and testosterone 5a-reductase.
Description
Phenazine is a free radical generator. It has been used as an electron transfer reactant in cell viability assays. Phenazine (10 μM) induces ssDNA break formation in the presence of the reducing agent NADPH in a cell-free plasmid cleavage assay when used at a concentration of 10 μM. It induces oxidative DNA damage in an alkaline comet assay and apoptosis in A375 melanoma cells when used at a concentration of 10 μM. Phenazine (20 nM) oxidizes cysteine-containing proteins in HepG2 cells.
Chemical Properties orange to light brown crystals or powder
Uses 5-Methylphenazinium methosulfate powder is used in tyrosine transaminase test and for enzymic determination of ethanol in blood by the colorimetric micromethod. Used with ascorbic acid to determine nitric oxide reductase activity. Since the reduced PMS is easily oxidized by oxygen, it is used in assays as an electron carrier between enzymes and oxygen, cytochrome c, indophenols, or tetrazolium salts. The reduced PMS is used as an electron donor to reduce cytochrome c or in photosynthetic experiments. Usage of PMS for detection of specific dehydrogenases has been reported.
Definition ChEBI: 5-methylphenazinium methyl sulfate is an azaheterocycle sulfate salt and a member of phenazines. It is used as an electron carrier in place of the flavine enzyme of Warburg in the hexosemonophosphate system and also in the preparation of succinic dehydrogenase.
Application
Phenazine methosulfate,5-Methylphenazinium methosulfate is a compound used to determine nitric oxide reductase activity. Phenazine methosulfate has been used:
as a component of succinate dehydrogenase enzyme substrate solution.
to induce superoxide radical generation in red blood cell suspensions and to study its influence on RBC deformability.
as a component of complex II histochemistry media.
Used in the discovery of potent bromophenazine antibacterial agents against Staphylococcus.
5-Methylphenazinium methosulfate powder Chemical Properties
Melting point 158-160 °C (dec.)(lit.)
density 1.3395 (rough estimate)
refractive index 1.6930 (estimate)
storage temp. -20°C
solubility H2O: 0.2 g/mL at 20 °C, clear, deep orange
form Crystalline Powder
color Dark yellow to brown or khaki
Water Solubility soluble in water (approximately 200 mg/ml).
Sensitive Light Sensitive
Merck 14,6109
BRN 3898869
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
CAS DataBase Reference 299-11-6(CAS DataBase Reference)
EPA Substance Registry System Phenazinium, 5-methyl-, methyl sulfate (299-11-6)
More Introduction:https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(19)68215-3/pdf