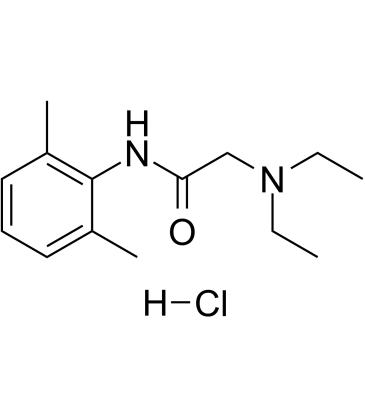
Lidocaine hydrochloride is characterized by strong penetration, strong dispersion, rapidly onset. The anesthetic performance is twice that of procaine and the toxicity is1. There is an anesthetic effect after 5 minutes treatments, and anesthesia can last 1 to 1.5 hours, 50% longer than procaine. The drug is effective on the heart of the disease or arrhythmia caused by cardiac glycoside, but on the supraventricular tachycardia is poor. This product is fast and oral ineffective, with short duration, and often used as intravenous administration.
Lidocaine hydrochloride uses
This medication is used on the skin to stop itching and pain from certain skin conditions (such as scrapes, minor burns, eczema, insect bites) and to treat minor discomfort and itching caused by hemorrhoids and certain other problems of the genital/anal area (such as anal fissures, itching around the vagina/rectum). Some forms of this medication are also used to decrease discomfort or pain during certain medical procedures/exams (such as sigmoidoscopy, cystoscopy). Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that works by causing temporary numbness/loss of feeling in the skin and mucous membranes.
How to use lidocaine HCl topical
If you are using the over-the-counter product to self-treat, read and follow all directions on the product package before using this medication. If you have any questions, consult your pharmacist. And if your doctor has prescribed this medication, use it as directed.
Before use on the skin, clean and dry the affected area as directed. Apply a thin layer of medication to the affected area of skin, usually 2 to 3 times a day or as directed.
If you are using the spray, shake the canister well before using. While holding the canister 3-5 inches (8-13 centimeters) from the affected area, spray until wet. If the affected area is on the face, spray the medication onto your hand and apply to the face. Do not spray near your eyes, nose, or mouth.
If you are using the foam, shake the canister well before using. Spray the foam onto your hand and apply to the affected area.
Lidocaine hydrochloride side effects
The incidence of adverse effect with lidocaine hydrochloride 2 was about 6.3%. Most adverse effects are dose dependent. Adverse effects are drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, burnout, euphoria, insanity, muscle convulsions, syncope, blurred vision, confusion and difficulty breathing. Large doses lead to severe sinus bradycardia, cardiac arrest, severe atrioventricular block and weakened myocardial contractility, reduced blood pressure and so on. Excess concentrations of lidocaine hydrochloride in the blood cause some problems. For example, atrial conduction slows, atrioventricular blocks (A-V-B), and inhibits myocardial contractility and cardiac output decreases. There are little allergic effects, such as erythema rash, angioneurotic edema and so on.
Additional information buy Lidocaine is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to local anaesthetics of the amide type and in patients with porphyria. Reactions due to overdose with lidocaine (high plasma levels) are systemic and involve the central nervous and cardiovascular systems. Effects include medullary depression, tonic and clonic convulsions, and cardiovascular collapse Solutions in multidose vials may contain hydrobenzoate derivatives and have been associated with allergic reactions in some patients. As with all of the amide local anaesthetics protein binding is reduced in the neonate (50% versus 64% in the adult), which necessitates reduced doses if adverse reactions are to be avoided.
Lidocaine hydrochloride Chemical Properties
Melting point 80-82°C
storage temp. Inert atmosphere,2-8°C
Water Solubility Water : ≥ 36 mg/mL (132.94 mM)
InChI InChI=1S/C14H22N2O.ClH/c1-5-16(6-2)10-13(17)15-14-11(3)8-7-9-12(14)4;/h7-9H,5-6,10H2,1-4H3,(H,15,17);1H
InChIKey IYBQHJMYDGVZRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILES C(NC1=C(C)C=CC=C1C)(=O)CN(CC)CC.[H]Cl
LogP 2.359 (est)
CAS DataBase Reference 73-78-9(CAS DataBase Reference)
EPA Substance Registry System Acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, monohydrochloride (73-78-9)
More Introduction:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lidocaine